Up until now the fastest was the mumps vaccine which took four years. As an example when vaccines are tested in clinical trials a control group similar to the vaccine recipient group in terms of age health status and other factors will not receive the vaccine.
 Ensuring The Safety Of Vaccines In The United States Cdc
Ensuring The Safety Of Vaccines In The United States Cdc
Testing vaccines is a complex process.

Vaccine testing process. This involves in vitro testing using individual cells and in vivo testing often using mice. Laboratory testing and development. These latter ingredients are included in most vaccines and have been used for decades in billions of doses of vaccine.
Before any vaccine testing or development begins scientists study the structure of the virus and how it causes disease in the body. The Vaccine Testing Process The development cycle of a vaccine from lab to clinic. But most vaccines typically take anywhere from eight to 15 years to develop test and produce.
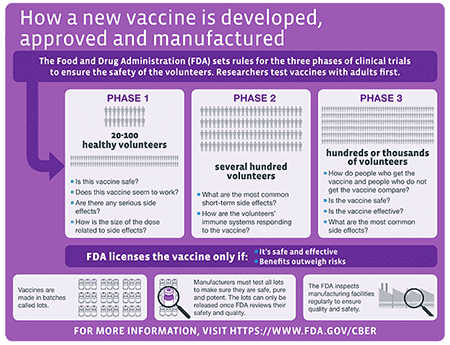
There are many layers of study and review that need to take place before a vaccine can be administered to a member of the general public. During a clinical trial a vaccine is tested on people who volunteer to get vaccinated. The scientists then conduct laboratory research to test their idea for a vaccine candidate.
Before a vaccine is ever recommended for use its tested in labs. FDA uses the information from these tests to decide whether to test the vaccine with people. The Traditional Vaccine Testing Process.
The creation of a vaccine involves scientists and medical experts from around the world and it usually requires 10 to 15 years of research before the vaccine is made available to the general public. How COVID-19 vaccines are being tested. Companies first make small batches and do small scale studies to characterise and optimise the production process.
Sometimes this testing occurs in animals. They also contain other ingredients to keep the vaccine safe and effective. This is considered the Research and Discovery Stage.
In many regards the evaluation of vaccines is the same as the process for. Scientists monitor VAERS reports to identify adverse events that. This process can take several years.
The first step of this extensive process involves several years of laboratory research in which scientists and. A vaccine are encouraged to submit reports to VAERS if they experience any adverse events after getting any vaccine. Next comes purity testing where the source materials and vaccine products are.
Phase I study an initial trial involving a small group of adult participants up to. Scientists test a new vaccine on cells and then give it to animals such as mice or monkeys to see if it produces an immune response. Researchers will compare the results of the vaccine and control groups in terms of side effects rates of infection and more allowing them to better understand whether the vaccine is safe and works.
They perform studies to determinate a suitable formulation that can keep vaccine components stable to the end of its shelf life. Scientists test a new vaccine on cells and. Standard vaccine development is a long process and studies are done in sequential steps.
Before a vaccine is registered for use it is tested extensively during development and then in thousands of people. Each vaccine component serves a specific purpose and each ingredient is tested in the manufacturing process. The vaccine testing process Vaccine testing is a complex multi-step process commencing with identity testing which ensures that the biologic is actually what it is meant to be.
The Science Behind Vaccine Research and Testing How Vaccines Are Made And Tested. The scientific evaluation of vaccines involves animal testing human clinical trials and post-approval surveillance. Clinical trials involve testing the vaccine in volunteers and are conducted in phases.
The Vaccine Testing Process The development cycle of a vaccine from lab to clinic. The vaccine has to pass rigorous safety tests at this stage and demonstrate that it works in animals. Testing first begins with laboratory research then animal studies and finally human clinical trials.
Almost two dozen vaccines are in various stages of testing around the world with one Modernas mRNA-1273 already showing promising results.






/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/45705452/mars-one.0.0.png)

